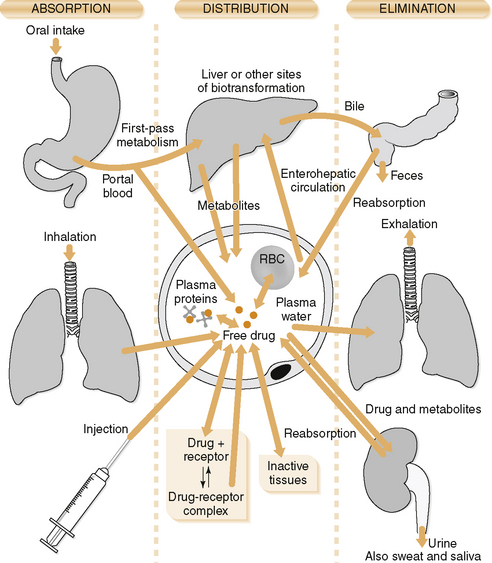
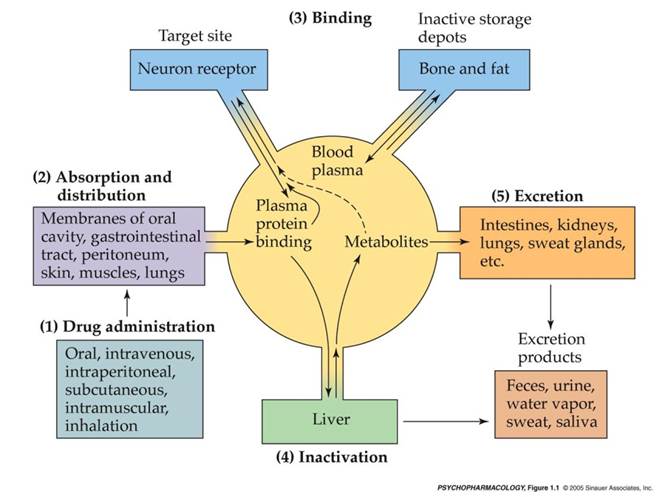
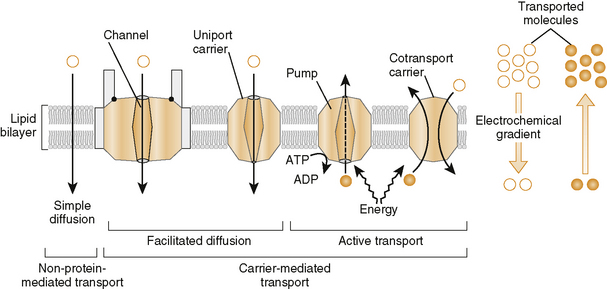
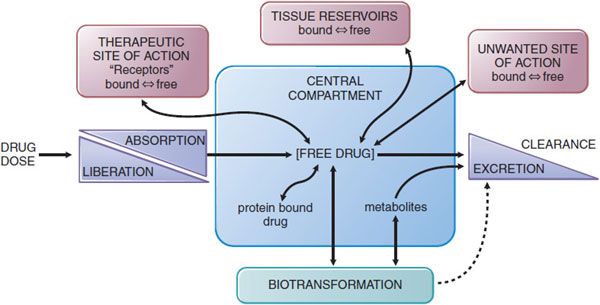
Chapter 2
MEDICINAL AND POISONOUS INGREDIENTS
Animal Based Ingredients:
Ambergris Physter catodom:
Uses: When aged, ambergris has a sweet earthy scent and can be used in ointments, creams, lincti and perfumes.
Beaver Castor fiber:
Uses: Beaver was consumed to treat eye, brain and nerve diseases. It was also believed to be an aphrodisiac.
Fish Oil and Omega-3:
Cod or shark liver:High in vitamin A (risk in pregnancy) and D
Tuna, salmon and cod body:High in omega 3 fatty acids, DHA and EPA.
Therapeutic uses: Anti-inflammatory, blood clots prevention to prevent, heart attack and stroke, reduce triglyceride and cholesterol levels, reduce high blood pressure and treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Side effects: Heart burn, diarrhoea, bad breathe and increased risk of bleeding in susceptible individuals.
Honey:
Uses: On wounds as an antiseptic and promote healing. It was also used in lincti to treat a cough.
Molluscs Strombidae and Muricidae:
Biome (tribe):Found: All over the world, but typically in tropical and subtropical waters.
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: The toxins from sea snails, cone shells and conch like were used as poisons. They were also used to treat seizures/epilepsy and pain in smaller doses.
Musk:
Therapeutic uses: The secretory glands from deer (Musk) were used in perfumes and as an aphrodisiac. Similar scents can be found in flora as well.
Pearl: Pinctada margaritifera:
Therapeutic uses: Treatment of eye disorders and depression
Toxins and venoms:
From any and all venomous or toxic creatures could be used therapeutically or as a poison based on the different types of effects listed in the overview.
Wax Cera Alba:
Therapeutic uses: Bees Wax is one of the ingredients used to make the base for creams and ointments, even today. It was also used for hair removal, wounds and skin conditions.
Inorganic Ingredients:
Alum: (AM(SO4)2, A = potassium or ammonium and M = aluminium or chromium.
Therapeutic uses: Alum was used to stop bleeding and inflammatory skin conditions. It was also used widely in tanning, cosmetics and in aftershave.
Arsenic
Therapeutic uses: Arsenic was widely used as a poison for human and vermin. It was also misused for its mild hallucinogenic properties which resulted in many fatal overdoses. It was also used to treat necrotic skin lesions and used in toothpaste to treat mouth ulcers, gum disease and tooth decay.
Bezoar stone
Therapeutic uses: General treatment for poisoning
Borax
Biome (tribe): Borax is an inorganic mineral often mined in arid climates (The Waerd and Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: It is a highly toxic substance, often used as a pesticide and poison. It was used as an antiseptic for cuts, bites, stings and wounds. It has also been used (and still is in certain circumstances) as a treatment for gynaecological infections such as yeast infections.
Copper and Cuprite
Therapeutic uses: The treatment of eye diseases
Haematite Also known as bloodstone and Rubrica sinopica [Fe2O3]
A black-grey and red-veined mineral containing about 70% iron.
Therapeutic uses: It was sometimes used as part of treatment for anaemia, especially due to blood loss and traumatic injury
Lapis Lazuli
Therapeutic uses: The treatment of hallucinations and psychiatric illness
Lead (white) compounds PbCO3 and Pb(OH)2
Therapeutic uses: In powder form or incorporated in to creams and ointments to treat skin itch
Mercury
Therapeutic uses: Used topically to kill parasitic skin infestations such as lice and fleas.
Potash (Potassium/Sodium Carbonate): K2CO3 and Na2CO3
Therapeutic uses: Treating dental problems, including toothache.
Salt
Therapeutic uses: Teeth cleaning and treating dental problems. It was also used as an antiseptic and as a purgative (induces both vomiting and diarrhoea).
Silver
Therapeutic uses: Topically as a powder and/or in creams as an antiseptic and mouthwash.
Sulphur
Therapeutic uses: In powder form or in a cream to treat skin itch, as an antiseptic and antibacterial and also to treat bites and stings.
Zinc
Therapeutic uses: In powder form or in creams to treat skin itch and skin infestations.
Plant Based Ingredients:

Adonis species:
Biome (tribe): Found in most places.
Therapeutic uses: Treating heart conditions, as a diuretic and for depression.
Poison uses: It can cause heart attacks, heart failure and cardiac arrest.
Almond: Amygdalus communis or Prunus amygdalus:
Biome (tribe): Originally found in subtropical, arid and semi-arid regions (The Waerd and Erishe), they later spread to most places.
Therapeutic uses: Sweet and Bitter Almonds have been used historically to treat migraines and eye ailments in seed form and oil form.
Sweet almond seeds have been used to treat fever, for pain relief (usually in combination with other ingredients). Sweet almond oil has been used as an aphrodisiac, a laxative (hopefully not at the same time), as a skin moisturiser and to treat inflammatory and infective skin conditions such as dermatitis and boils.
Bitter almond was used to treat gastrointestinal disorders, urogenital and gynaecological disorders of all kinds, including bladder and kidney stones, impotence, menstrual cramps.
Poison uses: Bitter almonds have approximately 50% of the oil content of sweet almonds and contain about 40 times the amount of cyanide compared to sweet almonds. An adult would need to ingest the equivalent of approximate 50 bitter almonds for a fatal dose of cyanide, where-as a child would only need to ingest 5 to 10.
Cyanide Poisoning: Mild to moderate toxicity includes nausea, vomiting, headache, weakness, confusion, dizziness and shortness of breath. Severe toxicity includes coma, respiratory failure, low blood pressure, seizures, and arrhythmias.
Aloe: Aloe sp:
Biome (tribe): Typically found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk)
Therapeutic uses: Used topically on the skin for wounds, eye and skin conditions.
Anamirta cocculus (seeds):
Biome (tribe): Found mostly in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: The picotoxin contained in the seeds can be used as an antidote to narcotic overdoses, such as barbiturates like sodium pentothal (truth serum) or phenobarbital, benzodiazepines like Valium/Diazepam, opioids like morphine. Abuse or recreational use: The seeds contain CNS stimulant chemicals which were abused to produce a “high” and giddy effect similar to being intoxicated with alcohol (yes, alcohol is a CNS depressant not stimulant).
Anise and liquorice: Pimpinella anisum (Apiaceae):
Biome (tribe): Typically found in tropical, semi-arid and arid regions (Janoa, To’resk, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: It is a common ingredient used to treat colic, stomach discomfort and gas. Historically these properties were often used for the treatment of dysentery.
Asphodel Asphodelus aestivus:
Biome (tribe): Mostly found in tropical, semi-arid and arid regions (Janoa, To’resk, The Waerd and Erishe).
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat chest pain associated with the heart and/or lungs. It was also be used to treat general joint aches and pains.
Astragalus: Astragalus membranous (root), Astragalus spp. Huangqi:
Biome (tribe): Mostly found in temperate and semi-arid regions (Neran, Kypiq, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Historically astragalus has been used as an immune booster to treat cold and flu, hepatitis and cancer.
Side effects and toxicity: It has potentially many and varied side effects. It is believed to reduce the effectiveness of immunosuppressant drugs and make associated conditions such as Rheumatoid Arthritis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Lupus Erythematosus and Multiple Sclerosis etc., worse.
Autumn crocus, Meadow Saffron or Naked lady Colchicum autumnale:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, To’resk, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: The source of the drug colchicine used to treat gout, Mediterranean fever and pericarditis by modifying the immune response.
Side effects and toxicity: The most common side effect of autumn crocus (colchicine) is vomiting and diarrhoea, but it can also be a very toxic poison.
Poison uses: It damages the kidneys and liver, nerves and muscles causing seizures, muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), respiratory failure and suppresses the immune system.

Autumn Skullcap Galerina marginate:
Has the same distribution and toxin as Death Cap mushroom. See Death Cap Mushroom
Balm Melissa officinalis:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq, maybe To’resk)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat anxiety, depression and psychotic illness.
Balm of Gilead Commiphora gileadensis:
Biome (tribe): Found in semi-arid and arid regions (The Waerd and Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat seizures and heart conditions.
Bamboo: Bambusa vulgaris:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras).
Therapeutic uses: Containing a large amount of silica, bamboo was burned as part of the extraction process for chalk. Chalk was historically and is still a common ingredient used in toothpaste. It was also used to relieve digestive distress associated with heart burn, reflux and diarrhoea, including dysentery.
The chalk powder/ash could also be used topically treat skin conditions especially itch.
Basil: Ocimum basilicum:
Biome (tribe): Found in dry, warm temperate and subtropical regions. (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: Basil has been used during medieval times to treat depression, scorpion stings and inflammation such as in creams and ointments for rheumatoid arthritis. It is also found with anise in colic remedies.
Some cultures used it as a calming agent for anxiety, nervousness and to aid sleep.
Ben tree Moringa peregrina:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical and subtropical regions (Neran, Janoa, To’resk, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: To stop bleeding and haemorrhaging
Bilberry: Vaccinium myrtillus:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, mountainous and alpine regions away from the sea (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, Brudvir) Therapeutic uses: Bilberry has historically been used to treat night blindness and vision loss associated with diabetic retinopathy. It is believed to increase blood circulation so may have benefits in people with poor circulation and conditions such as Reynaud’s Phenomenon.
Could this help tribes who are not used to cold climates?
It has been known to increase the risk of bleeding by reducing the ability of the blood to clot.
Bilberry is unsafe for use in pregnancy as it strongly stimulates uterine contractions.
Birthwort: Aristolochia species:
Biome: Found almost everywhere
Therapeutic uses: Historically used as a non-specific antidote to some poisons with variable effectiveness. It was also used to ease nausea associated with pregnancy and ease childbirth, urinary tract infections and menstrual cramps.
Black Cohosh: Cimicifuga racemosa:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate and cooler climates (Neran, Hrothi, Brudvir, Kypiq)
Historically Black Cohosh has been used to treat symptoms of menopause and menstrual cramps.
While not carcinogenic, it may worsen certain types of breast and ovarian cancer. It is also considered hepatotoxic (damaging to the liver) to some individuals.
Black Cohosh may cause nausea, vomiting, dizziness and weight gain.
Black Cohosh also reduces the metabolism of many other drugs/compounds so may increase their efficacy, side effects and toxicity.
Black Nightshade Solanum nigrum:
Biome (tribe): Primarily found in wooded areas (Brudvir, Janoa, Kypiq)
Poison uses: Berries contain a toxic chemical that is toxic to the cardiovascular system and CNS (central nervous system), resulting in nausea, flushing, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, paralysis, coma, cardiac arrhythmias and respiratory failure.
Borage Anchusa species:
Biome (tribe): Found almost anywhere.
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat hallucinations, depression, mania and psychotic symptoms.
Buttercup:
Clematis napaulensis:
Biome (tribe): Found in mountainous regions (Hrothi, Brudvir and Yoru).
Therapeutic uses: May be used to treat kidney disorders, including kidney stones.
Clematis orientalis:
Biome (tribe): Found in sunny areas of scrubland and forests near water, arid and semi-arid areas (Neran, Kypiq, Waerd and Erishe).
Poison uses: It can cause, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, muscle spasms, paralysis and damage to the liver.
Calabar Bean Physostigma venenosum:
Biome (tribe): Tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Uses: See Resurrection lily.
Camphor: Cinnamomum camphora:
Biome (tribe): Predominantly found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk).
Therapeutic uses: Preparations containing camphor (and invariably menthol as well) have been and are still widely used to treat the symptoms of the common cold and skin rashes including itch. Camphor has also been used historically to treat malaria, typhoid and general aches, pains, sore joints and muscles aches and pains.
Menthol and camphor are some of the most common ingredients in Vicks® products and many “heat” creams, ointments and liniments, along with various salicylate derivatives (see Willow). When applied vigorously, camphor produces a warming sensation to the area, while producing a cooling effect when applied gently.
Side effects and toxicity: In large doses, including on the skin, camphor is toxic causing seizures, rapid and/or irregular heart rhythm and muscle cramps/spasms.
Cannabis Cannabis sativa var. indica:
Biome (tribe): Found all over Kypiq forests because they are little stoners! (Jokes). With 12 to 13 hours of sunlight each day, it can grow almost anywhere and is well suited to wet environments (Neran, Kypiq, Janoa, To’resk, Dras, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Cannabis has been and is once again beginning to be used as a treatment for pain, seizures and eye conditions such as glaucoma.
Side effects and toxicity: blurred vision, hallucinations, increased appetite (munchies), amnesia, drowsiness, mood changes and psychosis.
Cerbera odallum species:
Biome (tribe): Primary found in swamps and marshy areas (Dras and To’resk).
Poison uses: A very toxic plant, whose poison can stop the heart by blocking calcium channels.
Chamomile: Matricaria recutita:
Biome (tribe): Typically found in temperate areas (Neran, Kypiq, To’resk).
Therapeutic uses: Historically used in creams and ointments to produce a localised anti-inflammatory effect. When ingested, in teas and oral liquids, it has also been used to aid sleep and reduce stomach cramps.
Christ’s thorn jujube Ziziphus spina-christi:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical, temperate, semi-arid and arid (Neran, Janoa, To’resk, Kypiq, The Waerd, Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat bee and wasp stings
Cinchona bark, Jesuits’ bark or Peruvian Bark Cinchona sp (Cinchonoideae)
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical areas (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Uses: The bark and its extracts Quinine and Quinidine can be used as treatment and prevention of Malaria (Quinine), night time muscle cramps (Quinine) and as an anti-arrhythmic agent (Quinidine)
Side effects and toxicity: blurred vision, sensitivity to sunlight, and other visual disturbances, angina (chest pain), slow–type heart arrhythmias, immune-mediated severe skin rashes and sunlight sensitivity (severe sunburning), liver toxicity and hepatitis, multiple blood disorders and dysfunction of the red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells/immune cells.
Citrus fruits:
Biomes (tribes): Found in tropical and subtropical regions (Janoa, To’resk)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to prevent scurvy and infection on long sea voyages. Also used to treat colds and flu
Clove: Eugenia caryophyllat:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used as a topical anaesthetic particularly for tooth ache and mouth ulcers. Also used in inhalants to treat symptoms associated with cough and cold.
Claviceps purpurea, Clitocybe dealbata, Clitocybe rivulosa and Conocybe filaris (Pholiotina rugosa) mushrooms:
Biome (tribe): Found in grasslands (Neran)
Side effects, toxicity and Poison use: The Clitocybe species have a poison similar to Wolf’s Bane: See Wolf’s Bane
Conocybe contain a poison similar to Death Cap Mushroom. See Death Cap Mushroom
Claviceps contains an ergotamine like substance which is a hallucinogenic similar to the psychedelic drug Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD, acid or “trips”). Ergotamine has been found to be effective in the treatment and prevention of migraines and depression.
Cornelian cherry Cornus mas:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used as a generalised antidote to poisoning
Costus Costus speciosus:
Biome (tribe): Found in wet, tropical, forested areas (Janoa, Kypiq, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Treatment for seizures and epilepsy
Cranberry: Vaccinium macrocarpon:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, cool temperate and higher altitude regions (Neran, Kypiq, Brudvir, Hrothi)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat and prevent scurvy on long sea voyages. It has also been used to treat and/or prevent urinary tract infections.
Excessive intake may result in diarrhoea, kidney stones and increased risk of bleeding in susceptible individuals.

Deadly Nightshade Atropa belladonna:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat pain, muscle spasms and cramps, motions sickness/vertigo, dangerously slow heartbeat, runny nose and insomnia
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: Deadly Nightshade is associated with blurred vision, dilated pupils and light sensitivity, rapid and irregular heartbeat, dry mouth, confusion, hallucinations, delirium and seizures.
Possible antidote for: Calabar Bean, Resurrection lily, Strychnine and Wolf’s Bane. These may also be possible antidotes to Deadly Nightshade poisoning.
Death Cap Mushroom Amanita phalloides:
Biome (tribe): Found in almost any wooded or forest region (Kypiq, Janoa, Brudvir)
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: Known as one of the most poisonous “toadstools”. The toxins are heat and cold stable so unaffected by cooking or freezing. They typically cause stomach upset and cramps, followed by in no particular order delirium, rapid heart rate, kidney failure, liver failure, heart failure/cardiac arrest.
There is no known cure, especially not in a medieval age, where victims/survivors invariably need liver and/or kidney transplants.
Destroying Angel’s Mushroom or other Death Cap mushrooms Aminata species: (11 species)
Similar biome and toxin to Death Cap Mushroom; See Death Cap Mushroom.
Devil’s claw: Harpagophytum procumbens:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, semi-arid and arid regions (Neran, The Waerd and Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Devils’ claw has been used historically to treat various forms of musculoskeletal aches and pain, including osteoarthritis and gout.
Side effects and toxicity: It has been shown to increase stomach acidity and increase the risk of stomach or duodenal ulcers. In large doses it has been associated with potentially dangerous effects on the rhythm of the heart.
Devil’s claw may also increase the risk of bleeding by reducing the clotting action of the blood and has been shown to affect the metabolism of many other drugs, resulting in increased risk of side effects and toxicity.
Devil’s (or Angel’s) trumpet Datura metel:
Biome (tribe): Found in warm tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Datura stramonium (another nightshade):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate areas (Neran, Kypiq)
Uses, side effects and poison uses: Similar to Deadly Nightshade; See Deadly Nightshade.
Possible antidotes: Calabar Beans, Resurrection lily, Strychnine, Wolf’s Bane
Dragon’s blood Dracaena draco (Dracaenaceae):
Biome (tribe) Found in subtropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras, Neran)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat wounds and stop bleeding
Dong Quai/Tang-Kuei/Dang Gui: Radix angelicae sinensis (root):
Biome (tribe): Cool high altitude mountains (Brudvir, Hrothi)
Therapeutic uses: Dong Quai has been used historically to treat symptoms of menopause and other gynaecological conditions. It has also been used to treat pain, inflammation and cardiovascular conditions.
Dong Quai extract has a naturally occurring chemical (furocoumarins) similar to other phytocoumadin compounds like warfarin with potent anticoagulant effects. This increases the risk of severe bleeding especially when used together with other blood-thinning agents.
Poison uses: could be used to cause death by slow bleed over time, or massive haemorrhage.
Echinacea: Echinacea purpurea, E.angustifolia or E.pallida (herb):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate and semi-arid (Neran, Kypiq, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Typically used to treat the common cold, cough and other viral infections. Sometimes used on wounds, bites and stings.
Side effects and toxicity: Generally well tolerated; however, in patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergies/hayfever and other immune mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and lupus erythematosus there is a risk of worsening these conditions
Echinacea also affects the metabolism of many drugs, increasing their metabolism and thus decreasing their effectiveness.
Ephedra or Ma Huang ¬Ephedra sp (Ephedraceae):
Biome (tribe): Found widely across relatively dry climates, in scrub, dry river beds, on sandy shores and river banks and on the side of mountains and even tundra, but not tropical, wetlands or swamps. (Neran, Kypiq, Brudvir, Hrothi, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: A sympathomimetic that mimics the effects of adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) to increase heart rate, blood pressure, metabolic rate.
Side effects and toxicity: headaches, insomnia, agitation/aggression, high blood pressure, dizziness, heart palpitations and rapid arrhythmias, heart attack, stroke, worsening heart failure.
Poison uses: In high enough doses, could be used to cause a heart attack, haemorrhagic stroke, arrhythmia and cardiac arrest.
Erythroxylum coca var (coca and ipadu) and Erythroxylum novogranatense var (novogranatense and truxillense):
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Erythroxylum species are the primary source of cocaine. Long before it was abused recreationally; it was used topically in creams, ointments and mouthwashes as a local anaesthetic for the skin, eye and mouth. Could be used as an anaesthetic to relieve pain or prior to surgery.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: In addition to its addictive nature and the sense of euphoria, it can cause agitation, hypertension (high blood pressure), tachycardia (rapid heart rate), arrhythmias, heart attack, cardiac arrest, seizures, stroke and depression (long term use and withdrawal)
Fennel: Foeniculum vulgare:
Biome (tribe): Found in most places
Therapeutic uses: One of the first known historical uses for fennel was as an antidote for some kinds of mushroom poisoning and snake bites. The severity of the poisoning or envenomation, and the effectiveness of fennel is unknown.
It was also believed to treat diseases of the brain, heart and liver, as well as being used for headaches and pain in general. It is another ingredient often used in colic remedies, to soothe crying baby.
Fenugreek Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fabaceae):
Biome (tribe): Found almost everywhere
Therapeutic uses: Ease stomach and digestive disorders and stimulates labour and lactation in new mothers.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: It is generally well tolerated; however, it has the potential to significantly increase the risk of serious and potentially life-threatening bleeding due to coumarin-like compounds (warfarin) contained within.
Feverfew: Tanacetum parthenium (leaf):
Biome (tribe) Found almost everywhere
Therapeutic uses: Acute and chronic migraine treatment and prevention. Also general aches and pains and pain associated with arthritis.
Is known to increase the risk of bleeding in susceptible individuals, similar in severity to aspirin and willow bark, but not as severe as anticoagulants such as warfarin and other coumarin compounds.

Foxglove Digitalis purpurea and Digitalis lanata:¬
Biome (tribe): Digitalis purpurea is mostly found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq), while Digitalis lanata can be found in woodland and on the side of mountains (Hrothi, Brudvir)
Uses: The Foxglove plant contains several different cardiac glycosides which can be very toxic. Digitoxin and Digoxin are the most common. They typically work by slowing the heart rate but increasing the force of contraction which is why they are primarily used in heart failure and atrial fibrillation (top chambers of the heart of quivering/spasming and not pumping/contracting properly)
Side effects and toxicity: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, confusion, slow heart rate and arrhythmia.
Galbanum Ferula galbaniflua:
Biome (tribe): Mountain slopes (Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat mental illness
Garlic: Allium sativum (bulb; preparations include aged garlic extract, powder, oil);
Biome (tribe): Mostly everywhere
Therapeutic uses: Historical use includes prevention of cold and flu. It may also possibly treat high blood pressure, cholesterol, and reduce blood clots.
Side effects and toxicity: Generally well tolerated, but excessive doses may cause increased risk of bleeding similar to that of aspirin and willow bark. It has been known to worsen asthma and cause life threatening allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
Ginger and Galangal: Zingiber officinale (Zingiberaceae):
Biome (tribes): Predominantly found in the tropics (Janoa, To’resk)
Therapeutic uses: A tonic for vitality, nausea and vomiting and as an aphrodisiac.
Side effects and toxicity: It is generally well tolerated, but may increase the risk of bleeding in susceptible individuals, similar to aspirin and willow bark extract.
Ginkgo Ginkgo biloba (leaf):
Biome (tribe): Found almost anywhere, best suited to moderately hot and summer environments.
Therapeutic uses: Ginkgo has been used historically to improved memory in dementia, prevention of vision loss, high blood pressure and treatment of tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Side effects and toxicity: Generally well tolerated, it may cause gastrointestinal upset (stomach ache, nausea, diarrhoea) and increases the risk of bleeding similar to aspirin and willow bark extract in excessive doses.
It is also known to affect the metabolism of drugs in unpredictable ways (multiple metabolic enzymes, some increased, some decreased) resulting in potential therapeutic failure or toxicity.
Ginseng Panax ginseng (Asian or Korean ginseng) and Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng) (root):
Biome (tribe): Found in cooler climates (Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to enhance physical performance and cognitive function. Possibly used to treat diabetes and aid weight loss.
Side effects and toxicity: Generally well tolerated, but may cause insomnia, gastrointestinal upset, racing heart or palpitations, increased blood pressure and reduced appetite.
Guarana Paullinia cupana (seed):
Biome (tribe): Tropical (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used as a stimulant, weight loss aid and aphrodisiac.
Side effects and toxicity: Generally well tolerated but may cause insomnia, high blood pressure, and seizures with excessive doses.
Hawthorn Crataegus laevigata, C. monogyna or C. folium (berry, flower or leaf):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: May provide benefit in treating chronic heart failure and to improve heart and cardiovascular function
Side effects and toxicity: May cause dizziness, fainting, low blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias.
Hellebore Helleborus niger and H. albus (Ranunuculaceae):
Biome (tribe): Wet, shady, cooler mountainous type areas are best (Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used historically to treat seizures, mania and psychiatric disorders.

Hemlock Conium maculatum:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate and subtropical regions near waterways (Neran, Kypiq, Janoa, Dras, To’resk)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used historically as a sedative and treatment for muscle spasms.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: A HIGHLY toxic poison commonly used historically to kill by causing paralysis and CNS depression, leading to respiratory failure.
Possible antidotes: Calabar Bean, Resurrection lily, Strychnine and Wolf’s bane. Likewise Hemlock may potentially be used as an antidote for these poisons.
Henbane Hyoscyamus albus, Hyoscyamus niger:
Henbane is similar to Hemlock. See Hemlock
Hyssop Hyssopus officinalis (Lamiaceae):
Biome (tribe): Found in warm sunny, temperate, tropical and semi-arid environments (Neran, To’resk, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat lung/chest infections, malaria, chronic coughs and as an antiseptic
Indian snakeroot or Devil pepper Rauvolfia serpentine:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions, plains and foothills (Janoa, To’resk, Dras, maybe Neran and Hrothi as well)
Therapeutic uses: Two of the several major chemical extracts include Reserpine and Yohimbine. They may be used for insomnia, high blood pressure, chorea or hyper-movement disorders (Huntingtons chorea), migraine prevention and psychiatric illnesses including catatonia and severe refractory depression.
Yohimbine has also been used as an aphrodisiac.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: Yohimbine as a poison has been associated with producing confusion, amnesia, short term paralysis and hallucinations
Don’t get the dose for poison and aphrodisiac mixed up or you might end up too confused, paralysed or just forget what you’re supposed to be doing.
Side effects and toxicity: nausea, vomiting, stomach ulcers, dizziness, angina (chest pain), fast and slow arrhythmias, seizures.
Iris Iris florentina L. or I. Mesopotamica (Iridaceae):
Biome (tribe): Found on sunny mountain slopes and steppe (Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Treatment of fevers, cough and cold, chest infections, wounds, colic and seizures.
Kava Piper methysticum (rhizome and root):
Biome (tribe): Tropical (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used historically to treat anxiety, insomnia and substance addiction.
Side effects and toxicity: It may cause blurred vision and other visual disturbances. In high enough doses it can cause temporary Parkinsonism like symptoms and movement impairment, increased risk of bleeding due to platelet dysfunction (blood won’t clot properly) and reduced immune system (susceptibility to infection) and liver failure resulting in death.
It strongly affects many other medications via metabolism causing reduced effectiveness.
Larkspur Delphinium brunonianum:
Biome (tribe): Found on stony mountain slopes and alpine areas (Hrothi, Brudvir, Yoru).
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: It is a poison which can cause paralysis, cardiac arrest and respiratory failure.
Possible antidotes: Calabar Bean, Resurrection lily, Strychnine and Wolf’s bane; likewise Larkspur may be used as an antidote to these poisons.
Lavender Lavandula officinalis or Stoachas Lavandula stoechas (Lamiaceae):
Biome (tribe): Found in dry sunny environments (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used historically to treat migraines, hallucinations, possibly psychiatric illness and as an antiseptic. Some cultures used Lavender as a general antidote for poisons with unspecified effectiveness.
Desert Lavander (The Waerd and Erishe)
Therapeutic uses : Used to treat cold and flu, infections, breathing problems like asthma, and as a sedative for epilepsy, anxiety and insomnia.
Lepiota species mushroom (5 in total):
Similar to Death Cap; See Death Cap.

Mandrake Mandragora autumnalis:
Biome (tribe): Commonly found in subtropical, arid and semiarid areas (Janoa, Dras, To’resk, The Waerd, Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat insanity and epilepsy, plus was used in creams topically to treat leprosy, and venomous bites and stings.
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: A HIGHLY toxic poison (leaves) similar to Deadly Nightshade.
Possible antidotes: Calabar Bean, Resurrection lily, Strychnine and Wolf’s bane; likewise, Mandrake may be used as an antidote to these poisons.
Milk thistle or St Mary’s thistle Silybum marianum (seed):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used historically to treat liver disease and as an antidote to hepatotoxic (liver) poisons.
Mint Mentha species:
Biome (tribe): Found everywhere
Therapeutic uses: A variety of oils such as peppermint and spearmint in addition to menthol have been used particularly with camphor to treat symptoms of cold and flu through inhalation and work by opening nasal passages and the sinuses to relieve congestion. Menthol is also used in “Heat” creams and ointments with camphor and other ingredients.
Common thyme or Garden thyme Thymus vulgaris is a type of mint that is often used as an antiseptic, particularly in mouthwashes for dental infections. Side effects and toxicity: In some individuals, it is known to cause a rash.
Myrtle Myrtus communis:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, semi-arid and arid areas (Neran, Kypiq, The Waerd, Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used for pain and inflammation similar to Willow. It has also been used in creams, ointments and liniments to treat spider bites and may be beneficial for other venomous creatures.
Myrobalan (cherry plum) Terminalia species (arjuana, citrina, chebula, bellerica, emblica):
Biome (tribe) Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat hallucinations, migraine, general pain and as an aphrodisiac. It could be used topically in creams and ointment to treat joint and muscle aches and pains.
Nerium Oleander:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical, subtropical and semi-arid regions (Janoa, Dras and The Waerd)
Therapeutically it has a very narrow therapeutic window, meaning you get toxicity at the same or close to the dose that might be used therapeutically. It has a mechanism of action similar to foxglove and other cardiac glycosides. See Foxglove
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: A poison that is toxic to the heart, potentially causing both fast and slow arrhythmias and cardiac arrest. Mortality is actually rare in adults, but in children and those susceptible to its effects (Brudvir) it can be lethal.
Except for Brudvir, Oleander might be a good non-lethal poison to incapacitate someone but not kill them..
Olive oil Olea europaea:
Biomes (tribe):Found almost anywhere but the extreme environments (NOT Yoru or Erishe).
Therapeutic uses: Used as an anti-inflammatory when ingested or used in a cream or ointment. It has also been used as a moisturiser when used in topical preparations
Opium poppy Papaver somniferum:
Biome (tribe) Found natively and best grown in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq) but can be grown anywhere.
Therapeutic uses: Most opioid alkaloids are used to treatment for pain, anxiety, insomnia and cough; however, papaverine which comes from the same plant can be used as a smooth muscle relaxant to treat impotence, kidney and gallbladder stones, cardiovascular disease (blockage of heart blood vessels causing angina), cerebrovascular disease (blood vessel blockage that may lead to stroke), peripheral vascular disease (poor circulation)
Side effects and toxicity: Increased heart rate and blood pressure, skin itch, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, seizures and priapism (not as great as you might think)
Priapism could be reversed with Ephedra before irreversible damage occurs, but it may worsen other side effects… see Ephedra
Peony Paeonia species:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate to alpine regions (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat seizures and psychiatric illness
Pine resin Pinus species:
Biome (tribe): Mostly found in temperate to subarctic regions (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, Brudvir)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat a cough in liquid form and is still used in creams and ointments as a moisturiser and to treat skin conditions particularly itch, inflammatory skin conditions and also wounds.

Podostroma cornu-damae
Biome (tribe): Found in mountainous alpine and subarctic regions (Hrothi, Brudvir, Yoru)
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: Although a different toxin, it has a similar effect to the Death Cap Mushroom; See Death Cap Mushroom.
Polypody Polypodium vulgare:
Biome (tribe): Mostly found in temperate (Neran, Kypiq)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used treatment of hallucinations and psychiatric illness
Red-behen (sea-lavender) Statice limonium:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, tropical and wetlands (Neran, Kypiq, Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat heart conditions and enhance male virility.
Resurrection lily Lycoris squamigera:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical and subtropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Prolongs and potentiates the effects of acetylcholine by blocking its metabolic breakdown by acetylcholinesterase. It is used in Dementia to improve memory and cognitive function. It could also be used to treat eye conditions such as glaucoma and conditions of muscle wasting/weakness such as myasthenia gravis.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: May cause, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, profuse sweating, stomach ulcer, dizziness, headache, muscle cramps and twitching, bradycardia (slow heart rate) and seizures.
Possible antidote for: Deadly Nightshade, Devil’s or Angel’s trumpet, Mandrake poisoning and possibly Henbane and Hemlock which are similar

Rhododendron aberconwayi:
Biome (tribe): Found in high mountainous areas (Hrothi, Yoru)
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: A poison that can cause hallucinations, haemorrhaging, liver and kidney failure
Safflower Carthamus tinctorius:
Biome (tribe): Found in arid and Semi-arid (Erishe and The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: has been used historically to treat some forms of poisonings and gynaecological and genitourinary conditions (kidneys, bladder and female reproduction organs).
Salep orchis species:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate regions (Neran, Kypiq).
Therapeutic uses: An antidote to some poisons and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases.
Sea squill Urginea maritima:
Biome (tribe): Found anywhere except arid and semi-arid (Not The Waerd or Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat heart conditions such as heart failure, or arrhythmia, kidney and bladder conditions.
Sedge (coconut grass) Cyperus Longus:
Biome (tribe): Found in wetlands and on the edge of lakes and rivers in other biomes (To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Treatment of heart conditions, including palpitations, arrhythmias, kidney and bladder conditions.
Skullcap Scutellaria lateriflora (leaf):
Biome (tribe): Found in wetlands (To’resk, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat anxiety, insomnia and epilepsy. It may cause giddiness and in excessive doses, stupor, confusion, delirium and coma.
NOT TO BE CONFUSED with the HIGHLY toxic Germander Teucrium species (they look alike) which will certainly result in liver failure and death.
St John's wort Hypericum perforatum (herb):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate and tropical regions (Janoa, Neran, Kypiq, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Predominantly used to treat depression and anxiety, but also used as an anti-inflammatory.
Side effects and toxicity: It affects the metabolism of just about every other drug known to Mann, reducing their effectiveness potentially resulting in treatment failure.
It also adds to the cumulative effectiveness and toxicity of other antidepressants and similar acting drugs used in the treatment of migraines, Parkinson’s disease and some pain killers.
It may cause restlessness, mania, muscle twitches, insomnia and in extreme cases agitation, aggression and hyperthermia.
Staphisagria (lousewort) Delphinium staphisagria (Ranunculaceae):
Biome (tribe) Found in temperate to semi-arid regions (Neran, Kypiq, The Waerd)
Therapeutic uses: Treatment of skin infections and infestations.

Strychnine tree Strychnos nux-vomica:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: Strychnine is a potent and highly toxic CNS stimulant. Typically produces seizures, muscle spasms and twitching, tonic-clonic seizures, arrhythmias, coma and death; however, since the brain and CNS are linked to everything, you can probably name it, and it will potentially cause that too.
Antidote: sedatives and supportive treatment to counteract any adverse effects that arise. Possibilities include: Deadly Nightshade, Devil’s or Angel’s trumpet, Mandrake and possibly Henbane and Hemlock.
Sweet basil Ocimum basilicum var. pilosum:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat heart conditions and nasal/sinus obstruction in cold and flu.
Tar made from the resins of pine, cedar and cypress trees:
Used for inflammatory skin conditions and skin itch; see pine resin.
Tea tree Melaleuca alternifolia (oil from leaf and branch):
Biome (tribe): Temperate and wetland areas, near rivers, streams and lakes (Neran, To’resk, Dras).
Endemic to Australia (pronounced Os-trar-ya in the native language, some bizarre mixed dialect of Tropical, Wetland and Desert locally called “Bogun”).
Therapeutic uses: Historically used as a mild antiseptic for skin infections, tinea, dandruff, acne, drop bear bites, great white associated limb amputation, croc-wrestling sprains, VB and/or goon induced cuts, bumps and abrasions.
Translation in to Proto-Neran
Drop bears = Koala bear
VB = Victoria Bitter: The finest lager you will find when the fridge is empty, the bottle-o is closed; you’re out of money and stranded in the middle of the Gibson Desert. A lager, fit for a penal colony (that’s penal not penile) and tastes just like it has been pre-drunk and physiologically recycled, then brewed again with old sweaty gym socks and jock straps
Goon = the cheapest, nastiest, box/cask wine or moonshine you can get your hands on
Bottle-o = the local purveyor of alcoholic beverages
Ok back to the being serious….
Tragacanth Astragalus gummifer:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, subalpine, highlands and desert with low water supply and full sunlight (Neran, Hrothi, Brudvir, The Waerd, Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: Used in modern pharmaceutics as an emulsifier and thickening agent in suspensions, syrups, and creams etc. it has also been used historically to soothe wounds and burns.
Tribulus Tribulus terrestris (leaf):
Biome (tribe): Found natively in warm temperate and tropical regions, but can survive in almost any environment (Neran, Kypiq, Janoa)
Therapeutic uses: Has been used for enhanced athletic performance, libido and impotence.
Side effects: Lots of babies and exhausted partner
Valerian Valeriana officinalis (root and rhizome):
Biome (tribe): Found in practically any environment except extreme heat (Not The Waerd or Erishe)
Therapeutic uses: It has been used to treat insomnia, anxiety, pain and seizures.
Velvet Beans Mucuna pruriens:
Biome (tribe): Found in tropical regions (Janoa, To’resk, Dras)
Therapeutic uses: Containing a relatively large amount of L-Dopa, it has been used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Side effects and toxicity: nausea and vomiting are common. Can cause high blood pressure, arrhythmias, heart attack, mania, psychosis and stomach ulcers.

Webcaps Mushroom Cortinarius species:
Biome (tribe): Found in all over the world in wooded and forested regions (Kypiq, Janoa, Brudvir):
Side effects, toxicity and poison uses: Typically causes irreversible kidney damage, leading to kidney failure and death.
No Known antidote
White-behen Centaurea behen (Asteraceae):
Biome (tribe): Found in subtropical, semi-arid and arid highlands
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat heart conditions including palpitations and enhancing male virility.
Willow Salix spp. (Salicaceae) (bark):
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate, alpine and arctic regions (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, Brudvir, Yoru)
Therapeutic uses: Pain, fever and inflammation.
Side effects and toxicity: May cause stomach ulcers and increases the risk of bleeding. Salicylates have been associated with fatal immune reactions associated with Reye’s syndrome in children with a recent history of viral infection such as cold and flu. The age considered safe varies depending on jurisdiction (some say > 12 years, others > 18 years).

Wolf’s bane, monkshood, devil’s helmet or aconite (root) Aconitum balfourii, Aconitum chasmanthum, Aconitum falconeri, Aconitum ferox, Aconitum heterophyllum:
Biome (tribe): Found in temperate lowlands to alpine highlands (Neran, Kypiq, Brudvir, Hrothi, Yoru)
Therapeutic uses: Historically used in lower doses for pain and inflammation, as a sedative, anaesthetic, treatment for irregular heart rhythm and treatment of a dangerously abnormal rapid heart rate.
Side effects, toxicity and poison use: A HIGHLY cardiotoxic (damages the heart) and neurotoxic (damages the brain and nerves) poison that also causes significant skin irritation and damage (contact dermatitis). Symptoms of poisoning include abnormal heart rhythm and slow heart rate, seizures, paralysis, coma and any number of heart and nervous system related conditions.
Possible antidote to: Deadly Nightshade, Devil’s or Angel’s trumpet, Mandrake poisoning and possibly Henbane and Hemlock which are similar.
Wormwood Artemisia species:
Biome (tribe): Mostly found in tropical and subtropical, arid and semiarid areas (Janoa, To’resk, Dras, The Waerd, Erishe).
Therapeutic uses: It has been used historically to stop bleeding, as an antiseptic and to cures paralysis.
Yew Taxus baccata:
Biome (tribe): Found in wooded areas within a variety of regions, but intolerant to poor-drainage and excessive water. (Neran, Kypiq, Hrothi, Brudvir).
Therapeutic uses: Historically used to treat heart problems, depression and cancer.
It could also be used as a poison, producing the highly toxic chemicals called “Taxanes”. In high enough doses, taxanes can cause nausea and vomiting, neurotoxicity, damaging the nerves and causing seizures, cardiotoxicity, damaging the heart to cause heart failure, arrhythmias involving irregular heart rate (speed) or rhythm (timing), damaging the lungs to cause respiratory failure and severe inflammatory skin reactions.